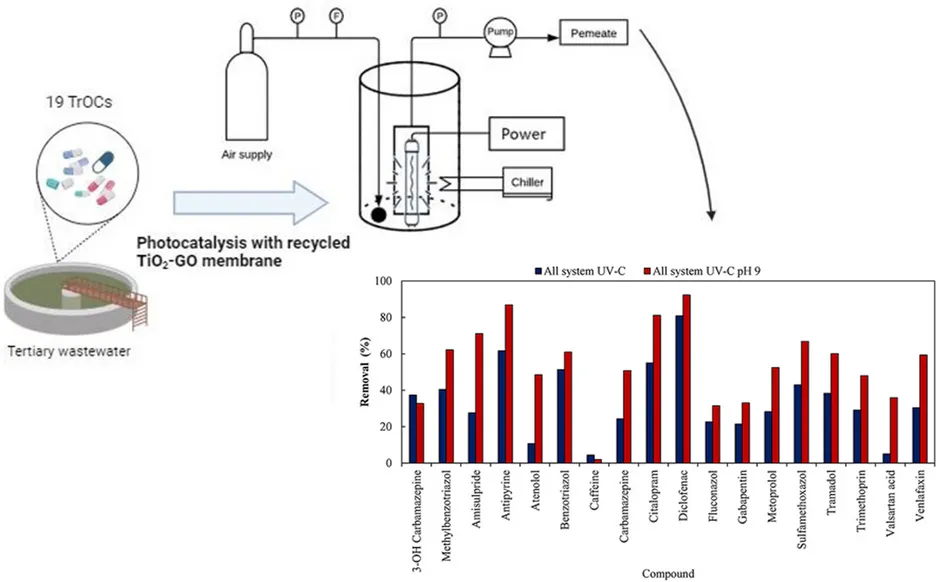
Photocatalytic membranes are a promising technology for water and wastewater treatment. Towards circular economy, extending the lifetime of reverse osmosis (RO) membranes for as long as possible is extremely important, due to the great amount of RO modules discarded every year around the world. Therefore, in the present study, photocatalytic membranes made of recycled post-lifespan RO membrane (polyamide thin-film composite), TiO2 nanoparticles and graphene oxide are used in the treatment tertiary-treated domestic wastewater to remove trace organic compounds (TrOCs). The inclusion of dopamine throughout the surface modification process enhanced the stability of the membranes to be used as long as 10 months of operation. We investigated TrOCs removal by the membrane itself and in combination with UV-C and visible light by LED. The best results were obtained with integrated membrane UV-C system at pH 9, with considerable reductions of diclofenac (92%) and antipyrine (87%). Changes in effluent pH demonstrated an improvement in the attenuation of TrOCs concentration at higher pHs. By modifying membranes with nanocomposites, an increase in membrane hydrophilicity (4° contact angle reduction) was demonstrated. The effect of the lamp position on the light fluence that reaches the membrane was assessed, and greater values were found in the middle of the membrane, providing parameters for process optimization (0.29 ± 0.10 mW cm−2 at the center of the membrane and 0.07 ± 0.03 mW cm−2 at the right and left extremities). Photocatalytic recycled TiO2-GO membranes have shown great performance to remove TrOCs and extend membrane lifespan, as sustainable technology to treat wastewater.