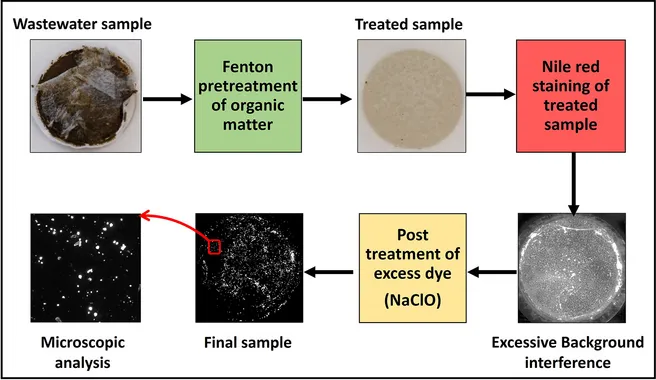
Efforts associated with common analytical techniques for microplastics including spectroscopic and thermo-analytical techniques are limiting the ability to perform large-scale monitoring of microplastics in the aquatic environment, because the analytical equipment required is costly and the analysis itself time consuming. Thus, there is a need to develop low cost, rapid alternative monitoring approaches. One possible alternative is the use of selective fluorescence staining of microplastic particles directly applied to environmental samples. However, to the best of our knowledge this has not yet been successfully implemented for wastewater samples. In this study, sludge samples are used as surrogates for wastewater alongside six different polymers to develop a combined sample preparation and staining protocol that could selectively stain microplastics without significant interference from the natural constituents of the sludge. Results confirmed that using Fenton's reagent to remove the organic matter before staining the sample with Nile red (NR) and subsequently bleaching it by sodium hypochlorite resulted in the best workflow to selectively stain microplastics and then analyze them in wastewater samples using fluorescence microscopy.