- Comparison of UV-AOPs (UV/H2O2, UV/PDS and UV/Chlorine) for TOrC removal from municipal wastewater effluent and optical surrogate model evaluation. Chemical Engineering Journal 362, 2019, 537-547 more…
- Role of reduced empty bed contact times and pre-treatment by coagulation with Fe(III) salts on the removal of trace organic compounds during sequential biofiltration. Science of The Total Environment 685, 2019, 220-228 more…
- Elucidation of removal processes in sequential biofiltration (SBF) and soil aquifer treatment (SAT) by analysis of a broad range of trace organic chemicals (TOrCs) and their transformation products (TPs). Water Research 163, 2019, 114857 more…
- Dynamik der Klarwasseranteile in Oberflächengewässern und mögliche Herausforderung für die Trinkwassergewinnung in Deutschland. , Ed.: Umweltbundesamt, 2018, more…
- UV/H 2 O 2 process stability and pilot-scale validation for trace organic chemical removal from wastewater treatment plant effluents. Water Research 136, 2018, 169-179 more…
- Evaluation of advanced oxidation processes for water and wastewater treatment – A critical review. Water Research 139, 2018, 118-131 more…
- Establishing sequential managed aquifer recharge technology (SMART) for enhanced removal of trace organic chemicals: Experiences from field studies in Berlin, Germany. Journal of Hydrology 563, 2018, 1161-1168 more…
- Removal of trace organic chemicals in wastewater effluent by UV/H2O2 and UV/PDS. Water Research, 2018 more…
- Microbiome-Triggered Transformations of Trace Organic Chemicals in the Presence of Effluent Organic Matter in Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR) Systems. Environmental Science & Technology 52 (24), 2018, 14342-14351 more…
- Evaluation of the short-term fate and transport of chemicals of emerging concern during soil-aquifer treatment using select transformation products as intrinsic redox-sensitive tracers. Science of The Total Environment 583, 2017, 10 - 18 more…
- Advancing Sequential Managed Aquifer Recharge Technology (SMART) Using Different Intermediate Oxidation Processes. Water 9 (3), 2017 more…
- Options and limitations of hydrogen peroxide addition to enhance radical formation during ozonation of secondary effluents. Journal of Water Reuse and Desalination 5 (1), 2015, 8--16 more…
- Influence of Wastewater Particles on Ozone Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants. Environmental Science & Technology 49 (1), 2015, 301-308 more…
- Evaluation of the persistence of transformation products from ozonation of trace organic compounds – A critical review. Water Research 68, 2015, 150 - 170 more…
- Evaluation of the persistence of transformation products from ozonation of trace organic compounds – A critical review. Water Research 68, 2015, 150-170 more…
- A hybrid process of biofiltration of secondary effluent followed by ozonation and short soil aquifer treatment for water reuse. Water Research 84, 2015, 315-322 more…
- Influence of Wastewater Particles on Ozone Degradation of Trace Organic Contaminants. Environmental Science & Technology 49 (1), 2015, 301-308 more…
- Ozonation products of carbamazepine and their removal from secondary effluents by soil aquifer treatment – Indications from column experiments. Water Research 49, 2014, 34 - 43 more…
- Evaluation of the prediction of trace organic compound removal during ozonation of secondary effluents using tracer substances and second order rate kinetics. Water Research 47 (17), 2013, 6467 - 6474 more…
- Optimized removal of dissolved organic carbon and trace organic contaminants during combined ozonation and artificial groundwater recharge. Water Research 46 (18), 2012, 6059 - 6068 more…
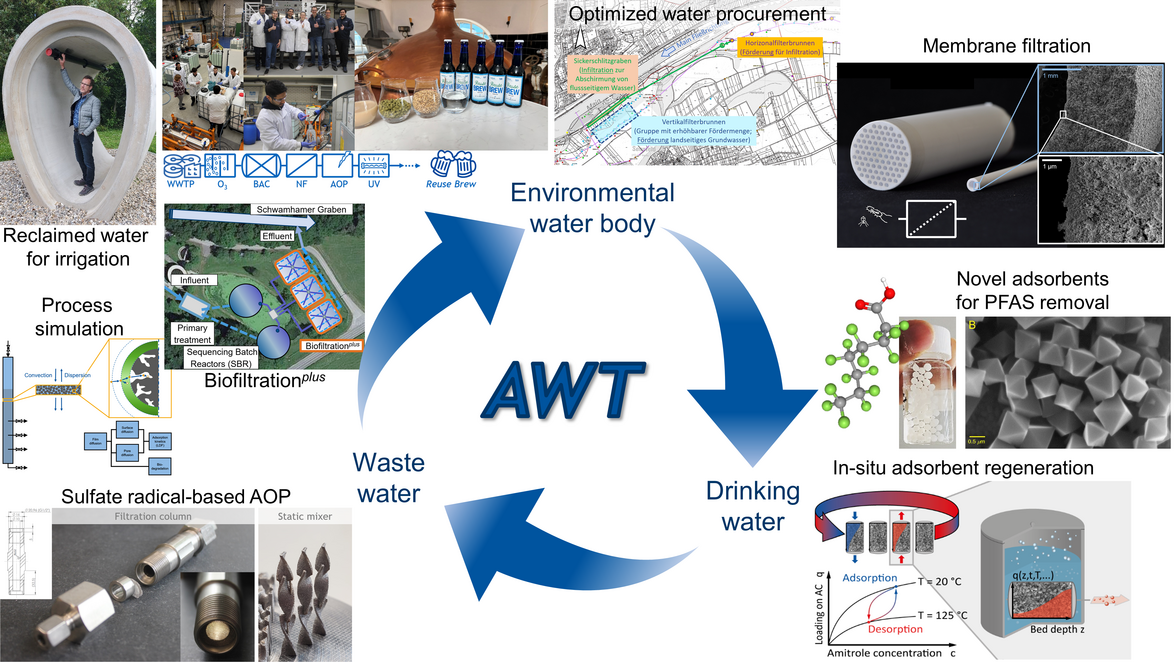
The research group deals with the question how to manage the anthropogenic water cycle and material cycles to supply water in sufficient quality and quantity for a growing world population in view of an accelerating climate change and attributed challenges. In the research projects we develop approaches that reflect closed water cycles contrasting the traditionally linear “take-make-waste” paradigm of centralized water supply and waste water discharge. Hence, advanced water treatment may be employed on either side, wastewater treatment or drinking water purification. This paradigm change is also propelled by current regulative initiatives, e.g. revision of EU Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive and EU regulation for agricultural water reuse. For advanced water treatment, combined or hybrid treatment processes are of paramount importance to remove trace organic chemicals at ng/L to µg/L level (e.g. pharmaceuticals, personal care products, industrial chemicals), and pathogenic microorganisms including antimicrobial resistances. Hybrid treatment processes relying on different physical, chemical and biological removal mechanisms offer the multiple barriers also against contaminants of emerging concern (CEC), e.g. persistent, mobile and toxic (PMT) substances or PFAS, and even unknown contaminants. In particular, we investigate hybrid treatment processes that combine separation and conversion, e.g. adsorption – biotransformation or membrane filtration – advanced oxidation or adsorption – advanced oxidation, or that combine different separation principles, e.g. activated carbon adsorption – ultrafiltration.
Adsorption:
- Improve the removal performance and process efficiency by adsorbent selection (e.g. activated carbons, zeolites, metal-organic frameworks), adsorber design and operation, and adsorbent regeneration/reactivation including in-situ and on-site regeneration
- Understand and model the transport and removal mechanisms of contaminants in complex water matrices leading to competitive adsorption
Membrane filtration:
- Mitigate and control fouling, e.g. organic fouling or biofouling, by pretreatment measures, e.g. UV irradiation, and feed channel and/or feed spacer design
- Improve the rejection of small, difficult-to-treat contaminants (e.g. antimicrobial resistance genes, pathogenic viruses for ultrafiltration or uncharged, low molecular-weight organic compounds for nanofiltration/reverse osmosis) by suitable process operational conditions and membrane selection
Oxidation and advanced oxidation:
- Evaluate the reactions of oxidants (e.g. ozone and radicals) with target contaminants (e.g. CECs or pathogens or antibiotic resistances) in water and wastewater matrices and optimize their process efficiency
- Develop and scale up emerging technologies, e.g. UV/chlorine, UV/persulfate and BDD electrodes
Natural and biological treatment processes, such as riverbank filtration, soil-aquifer treatment or biologically-active filters:
- Determine the key factors for the removal of CECs in natural systems and exploit them to improve process control
- Develop novel concepts for enhanced removal of CECs, e.g. sequential managed aquifer recharge technology (SMART)