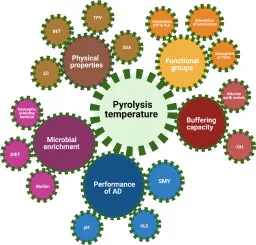
A comprehensive study was conducted to assess the influence of pyrolysis temperature (PyT) on the properties of biochar (BC) and its potential application in anaerobic digestion (AD). PyT is an essential parameter for effectively utilizing BC in full-scale AD, because PyT can develop BC properties that are necessary for improving AD performance through (I) the increment of BC porosity, (II) the adsorption and conversion of metabolites, (III) the enrichment of microbial communities, and (IV) the enrichment of functional groups. Some features of BC, such as porosity, electrical conductivity, and pore structure, increase consistently with increasing PyT. These properties have a positive effect on AD and enhancement of methane yield. The adsorption of excessive metabolites correlates with the enrichment of BC functional groups. The appearance of functional groups of BC decreases when the PyT increases. No substantial correlation (R2 < 0.1) could be found between the enhancement of methane yield and the enrichment of BC functional groups and the adsorption capacities of BC. Microbial communities are positively correlated to the increment of PyT with a moderate correlation (R) to the enhancement of methane yield. The review also identifies several knowledge gaps that necessitate further investigation.