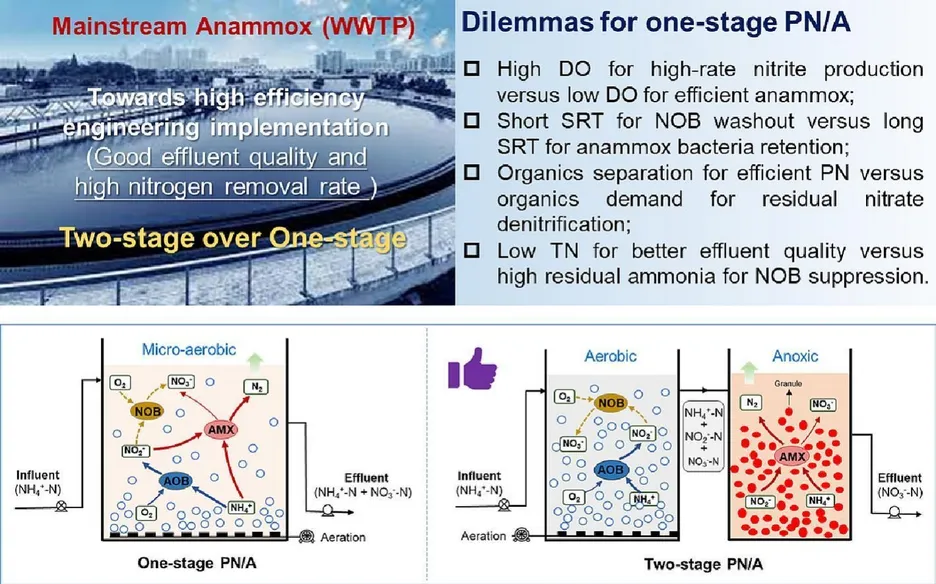
Partial nitritation-anammox (PN/A) process is known as an energy-efficient technology for wastewater nitrogen removal, which possesses a great potential to bring wastewater treatment plants close to energy neutrality with reduced carbon footprint. To achieve this goal, various PN/A processes implemented in a single reactor config-uration (one-stage system) or two separately dedicated reactors configurations (two-stage system) were explored over the past decades. Nevertheless, large-scale implementation of these PN/A processes for low-strength municipal wastewater treatment has a long way to go owing to the low efficiency and effectiveness in
nitrogen removal. In this work, we provided a comprehensive analysis of one-stage and two-stage PN/A processes with a focus on evaluating their engineering application potential towards mainstream implementation. The difficulty for nitrite-oxidizing bacteria (NOB) out-selection was revealed as the critical operational challenge to achieve the desired effluent quality. Additionally, the operational strategies of low oxygen commonly adopted in one-stage systems for NOB suppression and facilitating anammox bacteria growth results in a low nitrogen removal rate (NRR). Introducing denitrification into anammox system was found to be necessary to improve the nitrogen removal efficiency (NRE) by reducing the produced nitrate with in-situ utilizing the organics from wastewater itself. However, this may lead to part of organics oxidized with additional oxygen consumed in one-stage system, further compromising the NRR. By applying a relatively high dissolved oxygen in PN reactor with residual ammonium control, and followed by a granules-based anammox reactor feeding with a small portion of raw municipal wastewater, it appeared that two-stage system could achieve a good effluent quality as well as a high NRR. In contrast to the widely studied one-stage system, this work provided a unique perspective that more effort should be devoted to developing a two-stage PN/A process to evaluate its application potential of high efficiency and economic benefits towards mainstream implementation.
Neuer Zeitschriftenbeitrag von Cao et al., 2023