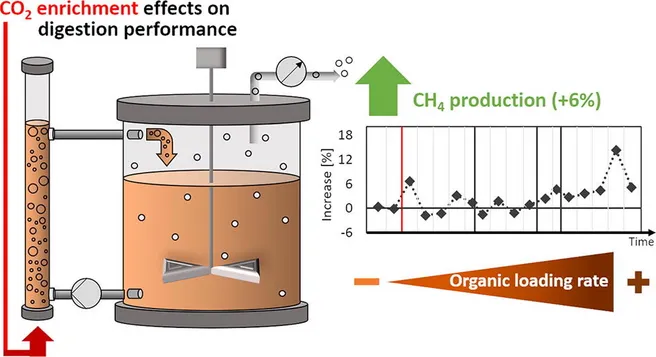
The effect of CO2 enrichment in sewage sludge anaerobic digestion (AD) as a potential strategy to improve the biogas yield was assessed at increasing organic loading rates (OLR). Effects on process performance and resilience were evaluated in long-term continuous AD experiments at lab-scale. The specific methane production (SMP) was sustainably enhanced in the test digester compared to a control at elevated OLRs, reaching an increase of 6 ± 12% on average at the highest OLR tested (4.0 kgVS/(m3·d)). The reduction of CO2 via homoacetogenesis, facilitating acetoclastic CH4 formation is proposed as the dominant conversion pathway. Results suggest that sufficient load of easily degradable substances is a prerequisite for intrinsic formation of the reduction equivalent H2 via acidogenesis. The enhanced resilience of the process under CO2-enriched conditions in response to acid accumulation further qualifies this approach as a viable option for improving AD performance by converting a waste stream into a valuable product.